All organizational strategies are constantly reviewed and revised. As the internal and external environments of an organization change, so should the company strategy to aid in the survival and growth of an organization. A standard process to evaluate the effectiveness of an organizational strategy is therefore essential. It ensures that the organization is on the right path and is constantly adapting in a dynamic market.
In this post, we will be explaining what strategy evaluation is and how to effectively implement the process.
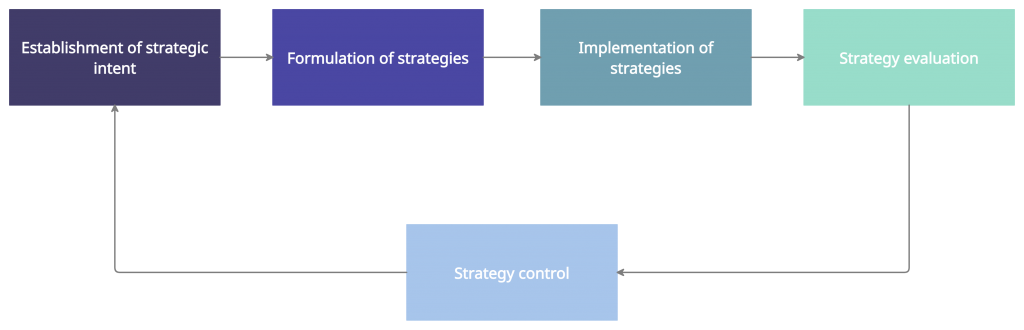
Strategic evaluation constitutes the final stage of strategic management and is considered one of the most vital steps in the process.

Strategy evaluation is the process by which the management assesses how well a chosen strategy has been implemented and how successful or otherwise the strategy is. To simply put, strategy evaluation entails reviewing and appraising the strategy implementation process and measuring organizational performance.
In the instance, the implementation of the strategy is not taking place as planned, say due to the limitations in the strategy that are blocking the achievement of organizational goals, necessary corrective actions should be identified and applied.
At the end of the evaluation, you’ll have gathered insight to either reformulate the strategy or to plan and develop new ones.
Evaluating the strategy helps improve it, distinguish between what works and what doesn’t, and contribute to the ongoing development and adaptation of the strategy to the changing conditions and complexities in the industry.
Strategy evaluation operates at two levels; strategic and operational. At the strategic level, the focus is given to the consistency of the strategy with the environment, and at the operational level, how well the organization is pursuing the strategy is assessed.
Through the process of strategy evaluation, strategists can make sure that the,
The stage of strategy evaluation requires the contribution of several participants who will be playing different roles throughout the process.
The board of directors: takes on the formal role of reviewing and screening the executive decisions in light of their environmental, business, and organizational implications. Although they are not directly involved in the evaluation and control of the strategy implementation process, they periodically take part in reviewing the organization’s performance and results.
Chief executives: are responsible for all the administrative tasks of strategy evaluation and control.
The SBU or profit-center heads: monitor strategy implementation at the business unit level and give feedback to the corporate parent who can intervene as necessary.
Financial controller, company secretaries, and external and internal auditors: responsible for operational control based on financial analysis, budgeting, and reporting.
Middle-level managers: carry out tasks assigned to them by SBU heads or the strategic planning group, and provide them with feedback and information. They will also be participating in the corrective actions, in the case of mid-term revisions in the implementation process.
The phase of strategy evaluation helps ensure that the implementation of the particular strategy will help the organization achieve its objectives. Without this step in the strategy management process, it would prove difficult to identify whether the strategy implemented is generating the desired effect. In addition, strategy evaluation also helps,
The strategy evaluation is carried out in order to determine that the strategy is helping the organization achieve its objectives. It compares the actual performance of the organization with desired results and provides the necessary insight into the corrective action that needs to be taken to improve the performance of the organization. Following are the steps in the process of evaluating strategy.
This step starts with determining what standards to set, how to set them, and the terms used to express the standards. To do this,
Performance indicators have to be set on the basis of quantitative or qualitative criteria in order to make measuring performance easier.
The standards of performance set will serve as the benchmark against which the actual performance will be evaluated. Based on these standards, managers should decide how to measure the performance and how often to do so.
The methods used to measure performance may vary on the standard set; usually, data such as the number of materials used, units produced, the monetary amount of services utilized, the number of defects found, processes followed, quality of output, and return on investment, are used.
Once the methods of measuring performance are identified, how often it should be done for control purposes needs to be then decided. Whether it should be on a daily, weekly, monthly, or annual basis is decided on factors such as how important the objective is to the organization, how quickly the situation might change, and how difficult or costly it would be to fix a problem once it has actually occurred.
Evaluating the actual performance against the standards of performance will reveal whether;
A predetermined set range of tolerance limits can be used to determine whether the results can be accepted satisfactorily. If the actual performance deviates from the budgeted performance within the set tolerance limit, the performance can be considered acceptable and the variance insignificant.
On the other hand, if the performance is below standards, effort must be directed to finding the root causes of the deviation and coming up with corrective action to fix it.
In the case the actual performance falls out of the tolerance limit, corrective action must be taken to solve it. The deviation can be caused internally or externally, predicted or random, or temporary or permanent.
If the actual performance is below the standards consistently, a thorough analysis should be carried out to find the root causes. If the organizational potential can’t meet the performance requirements, consider adopting attainable performance standards. In the case of an extreme deviation, you might have to consider formulating the strategy, which might require you to start from the beginning of the strategic management process.

Evaluating the effectiveness of a strategy entails assessing the internal and external forces that affect strategy implementation. Following are a few techniques that you can use to examine these factors and make well-informed strategic decisions.
A gap analysis is performed to identify and measure the gap between your current state of organizational performance and the desired state. It can be utilized to evaluate various aspects of the business from production to marketing.
Learn more on how to conduct a gap analysis and the tools you can use to accelerate the process and the gap analysis templates to simplify the steps.
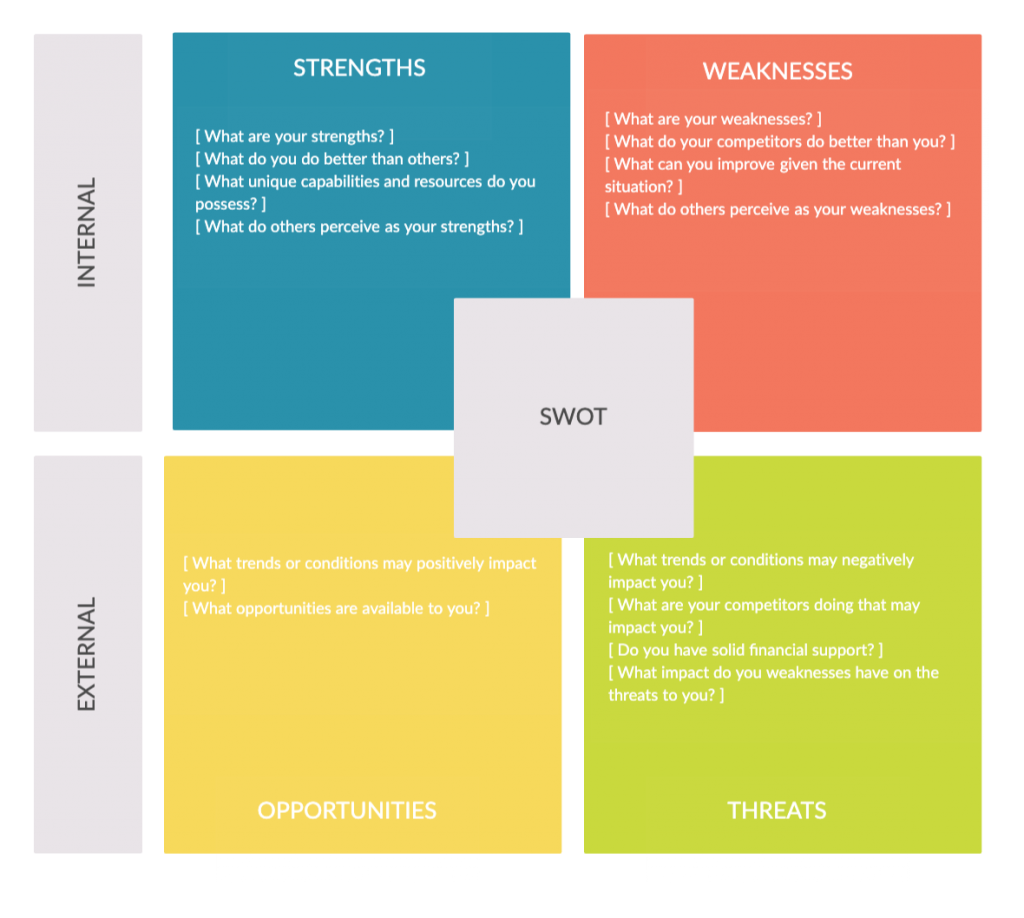
A SWOT analysis is another helpful tool that strategists use to assess the current situation -both internal and external environments – of an organization. It helps you gain insight into your internal landscape by analyzing strengths and weaknesses, and insight into your external landscape by scanning opportunities and threats.
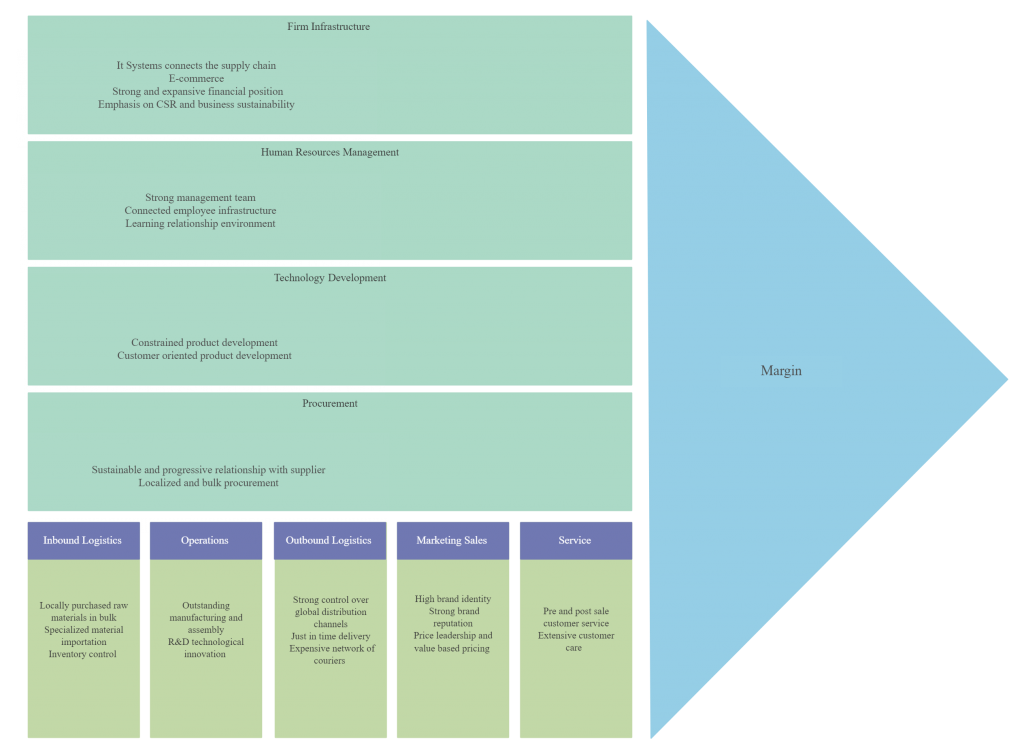
This analysis examines the set of activities the company performs to produce and market a product or service. It helps identify which activities are most valuable to the company and which needs to be improved to help perform better.
Strategy evaluation plays a significant role in assessing the effectiveness of a strategy in achieving organizational objectives and helping in the successful culmination of the strategic management process.
This guide gives an introduction to strategy evaluation and the steps to evaluating a strategy effectively, and we hope it will help you carry out the process seamlessly.
Let us know your experience in the comments section below.
Join over thousands of organizations that use Creately to brainstorm, plan, analyze, and execute their projects successfully.
Download our all-new eBook for tips on 50 powerful Business Diagrams for Strategic Planning. Get eBook Now